BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) is a condition that occurs when the calcium carbonate crystals in the utricle (a balance organ) of the inner ear become dislodged from their proper location and float freely within the semicircular canals. Its most striking symptom is a type of vertigo that is triggered by head movement, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Due to the anatomical position of the posterior canal, cases of posterior canal BPPV are more commonly encountered. However, because there are six semicircular canals in the inner ear and BPPV can occur in different patterns in various canals, there is no single maneuver that fits all cases; different maneuvers may need to be applied. The most effective treatment for BPPV is the canalith repositioning maneuvers, which are used to reposition the crystals. These maneuvers are performed by moving the head in a controlled manner at specific angles and provide rapid and effective results in most patients.
| Definition | A condition of vertigo that occurs due to the displacement of the otolith crystals in the inner ear and their migration into the semicircular canals. |
| Treatment Methods |
– Positional Maneuvers: Aim to remove the crystals from the affected canal and return them to their normal position. – Epley Maneuver: The most commonly used technique. – BBQ Maneuver – Gufoni and Appiani Maneuvers – Universal repositioning maneuver: https://advancedotology.org/en/universal-repositioning-maneuver-a-new-treatment-for-single-canal-and-multi-canal-benign-paroxysmal-positional-vertigo-by-3-dimensional-model-analysis-163740 – Semont Maneuver: An alternative method. |
| Home Exercises |
– Brandt-Daroff Exercises: Performed to improve balance and prevent recurrent attacks. – Cawthorne-Cooksey Exercises: https://www.webmd.com/brain/what-are-cawthorne-cooksey-exercises |
| Duration | Treatment is generally effective within a few sessions. Regular follow-up is recommended for recurrent cases. |
| Who Performs It? | It is performed by audiologists. |
| Complications | Temporary dizziness or nausea may occur after treatment. |
| Recommendations |
– Avoid sudden head movements. – Stay away from positions that increase the risk of dizziness. |
| Follow-up and Prevention | Regular check-ups, stress management, avoiding movements that trigger crystal displacement, and preventing dehydration. |
What Is BPPV and What Are Its Effects on the Inner Ear?
BPPV (Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo) is a condition that occurs due to the displacement of otoconia (ear crystals) in the inner ear, manifesting as sudden vertigo during head movements.
Balance organs in the inner ear:
- Semicircular Canals
- Utricle
- Saccule
These structures play a critical role in maintaining balance by detecting head movements and gravitational forces. The semicircular canals detect angular head movements, while the utricle and saccule are responsible for sensing linear head movements and gravity.
Effects of BPPV on the Inner Ear:
Normally, otoconia are found within the otolith organs (utricle and saccule). The dislodgement of otoconia from the utricle into the semicircular canals leads to the development of BPPV.
Since the otoconia alter the mass of the semicircular canals, they cause the inner ear to generate incorrect signals in certain head positions. Consequently, corrective eye movements, known as nystagmus, occur. The formation of nystagmus is actually a compensatory mechanism; however, it also causes the patient to perceive a severe spinning sensation.
Frequently occurring cases of BPPV that are not properly treated or remain untreated over time may become chronic, leading to significant problems in an individual’s quality of life. These chronic cases may eventually evolve into Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness (PPPD).
What Are the Common Symptoms of BPPV?
BPPV manifests with bothersome symptoms triggered by changes in head position, which can negatively affect an individual’s quality of life. The most common symptoms are listed below:
- Sudden spinning sensation
- Involuntary eye movements
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Imbalance while walking
- Risk of falls
- Sweating/palpitations
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty focusing
These symptoms arise from the displacement of the crystals in the utricle into the semicircular canals. Movements such as turning in bed upon waking, sudden bending, or lifting the head upward can trigger these symptoms. During severe attacks, the person may have difficulty performing daily activities and may feel insecure.
Furthermore, in elderly individuals, these symptoms may become more pronounced and lead to more serious consequences due to the risk of falls. However, with accurate diagnosis and effective treatment methods, this condition can usually be controlled and the symptoms can be greatly reduced.
How Is BPPV Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of BPPV is made by thoroughly evaluating the patient’s complaints and performing various physical tests. The characteristics, duration, and triggering factors of the vertigo attacks are carefully examined:
- Vertigo triggered by head movements
- Short and recurrent attacks
- Absence of hearing loss or neurological symptoms
Physical Examination:
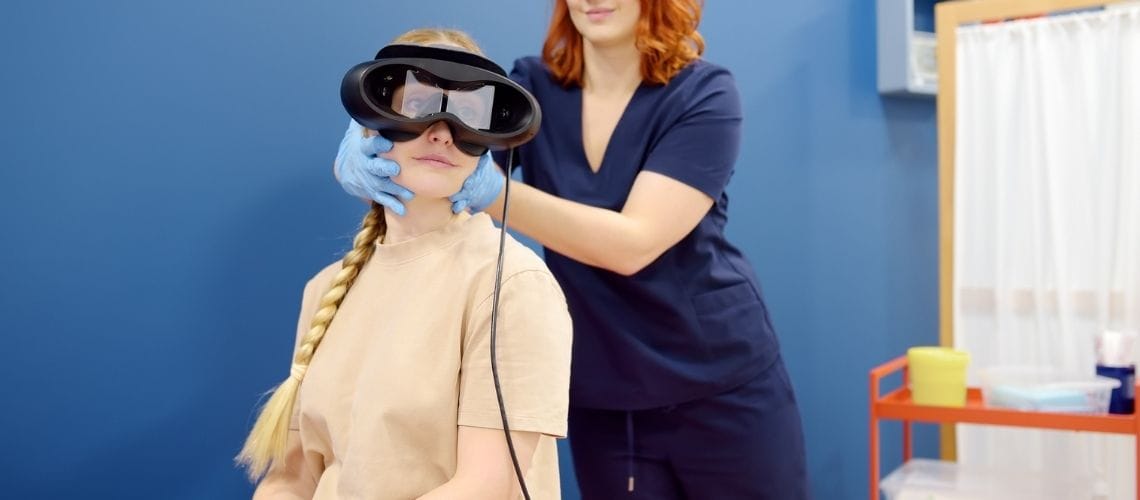
- Physical examination is aimed at determining whether there is another cause for the vertigo. Detailed evaluations by ENT specialists, along with cardiovascular and neurological assessments, are conducted. Generally, the patient appears normal during rest. In audiology laboratories, diagnostic tests are performed by audiologists using special equipment (such as VNG or Frenzel goggles).
Diagnostic Tests
- The Dix-Hallpike test is the most widely known test and is used in the diagnosis of posterior canal BPPV.
- For anterior canal BPPV, the Head-Hanging test is used,
- and for horizontal canal evaluation, the Roll test and Bow-Lean tests are the most commonly used differential diagnostic tests.
In these tests, the patient’s head is positioned at specific angles according to the canal being evaluated. Nystagmus and vertigo are observed in these positions. The nystagmus, which is the objective finding of the vertigo, exhibits various characteristics such as pattern, duration, and phase.
Additional Tests
If nystagmus is present but does not display a pattern specific to the affected canal, or if neurological symptoms are present, the evaluating audiologist may deem it necessary to apply different tests and conduct further evaluations. VNG is a medical device that allows for the application of a broad test battery. With the VNG device, eye movements are recorded and analyzed. Additionally, if needed, other tests such as VEMP and v-HIT may be performed to rule out other pathologies and assess the inner ear capacity. In necessary cases, imaging methods such as MRI and CT are applied:
- VNG
- VEMP
- v-HIT
- Audiological Evaluations
- MRI or CT (in suspicious cases)
The diagnosis of BPPV is generally confirmed through simple examinations and tests. However, differential diagnoses become important in more complex cases.
What Are the Effective Treatment Methods for BPPV?
In the treatment of BPPV, various maneuvers are applied to reposition the otoconia in the inner ear to their correct location. These methods are determined based on which canal is affected by the disorder and usually result in high success rates.
- Epley Maneuver: Uses head and body movements to reposition the otoconia from the posterior canal to their correct position.
- Semont Maneuver: An effective method for the posterior canal that uses rapid movements to return the crystals to their proper position.
- Gufoni or BBQ Maneuver: Used in the treatment of horizontal canal BPPV; it is an effective and simple method.
- LemYazıyı Puanlayın![Toplam: 0 Ortalama: 0]

Dr. Audiologist Emel Uğur was born in 1982 in Çanakkale. She worked for 15 years at Istanbul Training and Research Hospital, specializing in Pediatric Audiology, Otologic Diseases, and Vestibular System Disorders. In 2015, she joined the Acıbadem Healthcare Group. She currently works as a Dr. Audiologist at Acıbadem Altunizade Hospital and also serves as a faculty member and program director of the Audiometry Department at Acıbadem University Vocational School of Health Services.






Location of our clinic in Istanbul, Turkey