Videonystagmography (VNG) Test
Videonystagmography (VNG) is the general name for the device and the tests used to investigate the etiology of dizziness by recording eye movements through a special set of glasses equipped with infrared cameras.
The tests performed with VNG are used to distinguish whether dizziness and balance disorders are of peripheral or central origin. In cases of peripheral diseases, it is used to diagnose the specific disorder, determine the presence of vestibular hypofunction, and, if present, ascertain whether it is unilateral or bilateral. VNG tests can be grouped into oculomotor tests, static positional tests, dynamic positional tests, and specific diagnostic tests.
VNG prioritizes patient comfort, is painless, and is a non-invasive method (it does not compromise body integrity). Considering the test techniques and technologies used, it is both reliable and comfortable for the patient.
Description | A battery of tests that evaluates the balance system between the inner ear and the brain by recording eye movements. |
Purpose | To detect the causes of vertigo, dizziness, and balance problems. |
Procedure | Eye movements are monitored with special glasses while various positions, temperature changes, and visual stimuli are applied. |
Test Components | – Spontaneous Nystagmus Test: Evaluates the natural state of eye movements. Oculomotor measurements Static positional tests – Positional Tests: Measure responses to head movements. – Caloric Test: Assesses the balance response by stimulating the ear canals with warm and cold air or water. |
Who Is It For? | Patients with complaints of vertigo (dizziness), balance disorders, or double vision. |
Preparation | Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and certain medications before the test. Follow the instructions provided by your doctor. Wear comfortable clothing when coming for the test. |
Duration | Approximately 60-90 minutes. |
Risks | It is a non-invasive test and does not carry risks; however, temporary dizziness or nausea may occur. |
Advantages | Helps distinguish between problems originating from the inner ear and those from the central nervous system. |
Interpretation of Results | The test results provide information about the function of the balance and vestibular systems, which aids in planning appropriate treatment and rehabilitation. |

Doctor Audiologist Emel Uğur
Dr. Audiologist Emel Uğur was born in 1982 in Çanakkale. During her 15-year tenure at Istanbul Training and Research Hospital, she primarily worked on Pediatric Audiology (Hearing Loss in Infants and Children), Otological Diseases (Ear Diseases and Hearing Health), and Vestibular System Disorders (Vertigo and Imbalance). In 2015, she joined the Acıbadem Healthcare Group.
About Me
How Is Evaluation Performed in VNG?
The inner ear balance system is a specialized sensory organ composed of structures sensitive to all types of angular and linear head movements. Every head movement made by an individual is detected by the inner ear. During this process, the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) is activated to produce compensatory eye movements. This keeps the visual field stable and ensures clear, sharp vision.
VNG is based on the operating principles of the VOR reflex. The tests performed for this purpose include:
- Oculomotor tests,
- Static positional tests,
- Dynamic positional tests,
- Specific diagnostic tests
What Is Nystagmus?
Nystagmus is the involuntary, jerky movement of the eyes that occurs as a VOR response. It appears in three forms:
- Spontaneous Physiological Nystagmus
- Induced Nystagmus
- Pathological Nystagmus
*We recommend filling out all fields to ensure the best response.
When Is VNG Necessary?
The VNG test should be performed on every patient presenting with complaints of imbalance or dizziness. Approximately 80% of patients presenting to the emergency department with dizziness have issues originating from the inner ear. This highlights the high diagnostic value of the test. Additionally, it is an important diagnostic tool in the differential diagnosis of central versus peripheral imbalances and dizziness.
It is especially necessary for individuals with chronic balance problems to undergo this test for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. In addition to its high diagnostic value, VNG is also used in conjunction with VEMP, v-HIT, and mandatory audiometric evaluations to gather detailed data about the inner ear.
- Balance problems
- Dizziness (Vertigo)
- A feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears
- Lightheadedness
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Which Diseases Does the VNG Test Diagnose?
The videonystagmography test plays a critical role in diagnosing various health problems related to balance. It is used to detect specific peripheral (inner ear) and central (central nervous system) pathologies. Here are some of the diseases that can be diagnosed with the VNG test:
- BPPV (Canalithiasis): Identifies transient vertigo triggered by head movements.
- Labyrinthitis: Characterized by sudden hearing loss and sudden balance loss due to inflammation in the inner ear.
- Ménière’s Disease: Arises from an increase in endolymphatic fluid in the inner ear, characterized by fullness in the ear, hearing reduction, and episodic vertigo.
- Vestibular Neuritis: This test provides important information in cases of vestibular nerve inflammation.
- Acoustic Neuroma: Necessary for determining the level of functional weakness caused by tumors on the vestibular nerve. The data obtained forms the basis for planning vestibular rehabilitation.
How Does the Video Eye Movement Test Work?
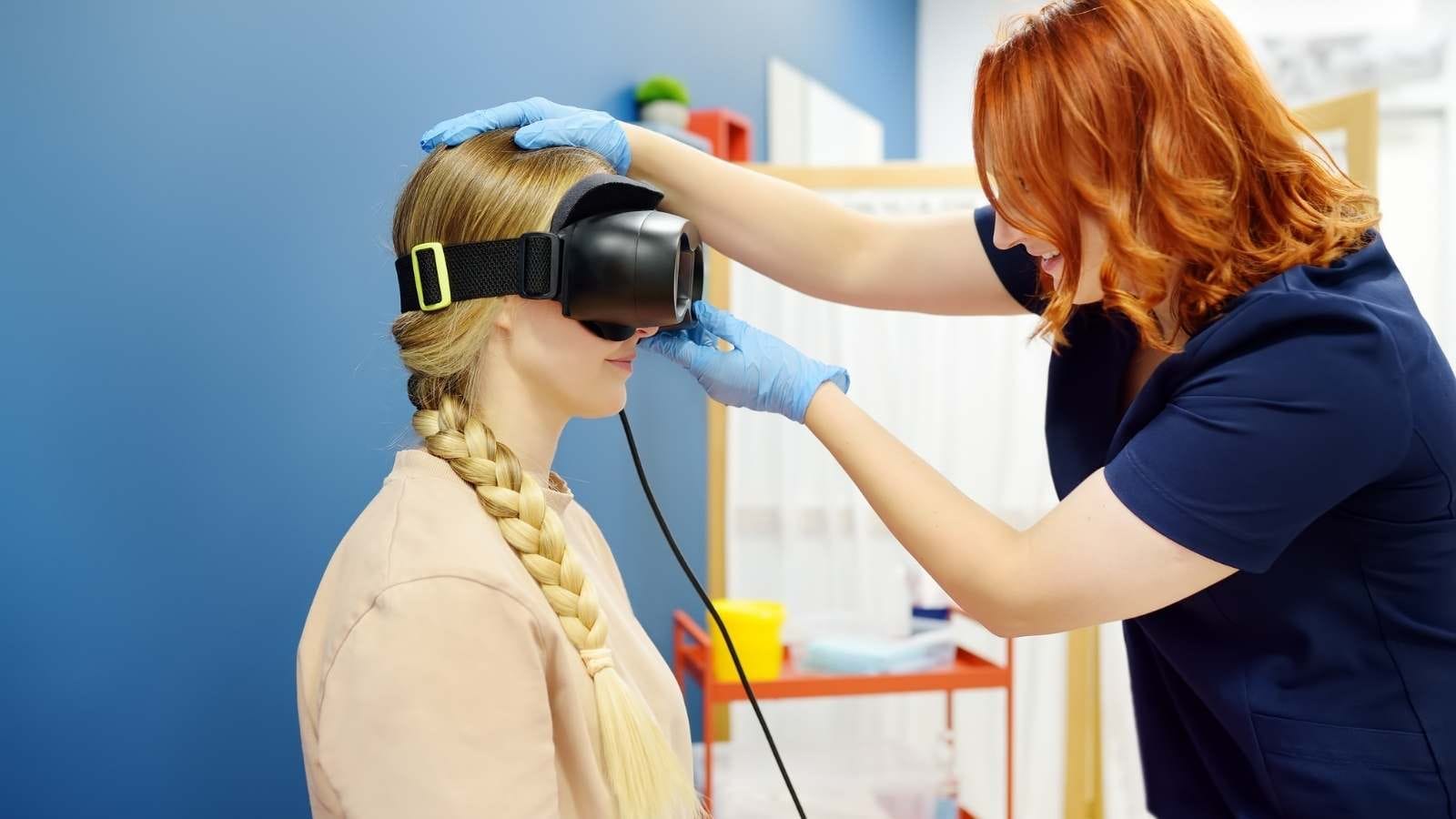
The videonystagmography test works by recording eye movements. During the test, patients wear a special pair of glasses in a dark room. The infrared cameras in the glasses record the eye movements in detail. Audiology specialists use various stimuli to analyze the patient’s eye movements and the activity of the VOR arc.
How Do You Prepare for the Video Eye Movement Test?
Preparation for the videonystagmography test is generally simple and patient-friendly. A detailed history is taken from you before the tests. Your medication usage is also reviewed because some medications have a vestibulo-suppressant effect. These medications can alter the test findings within normal limits and may conceal the underlying pathology. In such cases, you may need to pause your medication use a few days before the test. This step is critical as your medications can affect the test results. Here are the types of medications and supplements you need to report:
- Prescription medications
- Over-the-counter medications
- Herbal supplements
It is also recommended to wear comfortable clothing on the day of the test. If possible, having a companion accompany you is important. These preparations ensure that the test is conducted accurately and comfortably.
For the tests, the VNG goggles are placed on your eyes. Calibration is performed before the test. An audiology specialist will guide you through each test and prepare you for the procedure.
Contact us for detailed information and appointments!
What Should I Expect During the Videonystagmography Test?
During the videonystagmography test, the patient wears specially designed goggles and sits in a dark room. The test is based on recording eye movements and consists of three main sections:
Ocular Test:
- The eyes fixate on stationary lights.
- They follow moving lights.
Positional Test:
- The head and body are moved into different positions.
- Specific head movements are observed.
Caloric Test:
The caloric test is based on recording and analyzing the functional changes that occur when the endolymphatic fluid in the inner ear is warmed and cooled. It has very high diagnostic value and evaluates the functional symmetry between the two ears.
During the test, warm and cold stimuli (air or water) are applied sequentially into the external auditory canal using an otoscope placed by the audiology specialist. For each stimulus, the test duration is approximately 2 minutes—the first minute for stimulation and the second minute for recording responses. Between tests, a break of about 5 minutes is given to allow the inner ear to return to its normal temperature. Therefore, the caloric test alone can take approximately 20-25 minutes. The patient may experience dizziness during this time. This dizziness is expected and desired, and it resolves immediately after the test.
In each section of the test, the recorded nystagmus (involuntary eye movements) is analyzed. While performing these tests, audiologists take all necessary measures to ensure the patient’s comfort. Additionally, the patient does not feel any pain during the test. All symptoms triggered by the test subside within 2 minutes after the test is completed.
What Do the Videonystagmography Results Mean?
The fact that some or all of your videonystagmography results are normal or abnormal can have different implications regarding peripheral or central pathologies. The specific diagnostic characteristics of the pathology in each test provide differential diagnostic clues. Additional balance tests, audiometric evaluations, and even radiological examinations may be necessary until a definitive diagnosis is reached.
Frequently Asked Questions

VNG and Calibration
Any pathology detected during the oculomotor tests in VNG evaluations carries significant diagnostic value. Therefore, it is essential to perform calibration before starting the VNG tests.
In which two positions is calibration performed for the VNG test?
During the VNG test, calibration is performed based on the horizontal and vertical planes to ensure that the patient’s eye movements are recorded accurately. The most accurate position for calibration is when the patient is seated and positioned exactly in the midline at a distance of 1.2 meters from the stimuli.
Why is the VNG test requested?
The VNG test is a comprehensive evaluation used to assess the vestibular system. It evaluates the functional status of the balance organs in the inner ear and the reflexive connections between the inner ear and vision, especially in patients with symptoms such as dizziness and imbalance.
These evaluations have diagnostic significance. In addition, when extra symptoms such as tinnitus or a feeling of fullness and pressure in the ears accompany vestibular disorders, a VNG test is absolutely necessary. The evaluations not only serve a diagnostic purpose but are also invaluable for determining the vestibular rehabilitation program. Therefore, the VNG test is important both for diagnosis and for planning treatment.
How long does the VNG test take?
The VNG test is a process that evaluates the eye movements of participants. During this time, eye movements are recorded and analyzed using various stimuli. Therefore, the total time expected to complete this test is approximately sixty minutes. This duration covers the entire period from the beginning to the end of the test. In some cases, additional tests may be added to the VNG battery, which may extend the duration slightly.
How much does the VNG test cost?
The cost of the VNG test varies depending on the technical equipment of the hospital. Additionally, the purpose for which the test is performed affects the pricing. Factors such as test duration and other tests performed simultaneously also influence the cost. For these reasons, it is difficult to state a definitive price for the VNG test. It is recommended that patients consult with their chosen healthcare facility for the most accurate information.





